Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Chemical Name
- Tilley Product Number
- Plastics & Elastomers Functions
- Technologies
- Product Families
Features & Benefits
- Materials Features
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Base Chemicals End Uses
Properties
- Physical Form
Technical Details & Test Data
- Viscosity vs. Temperature
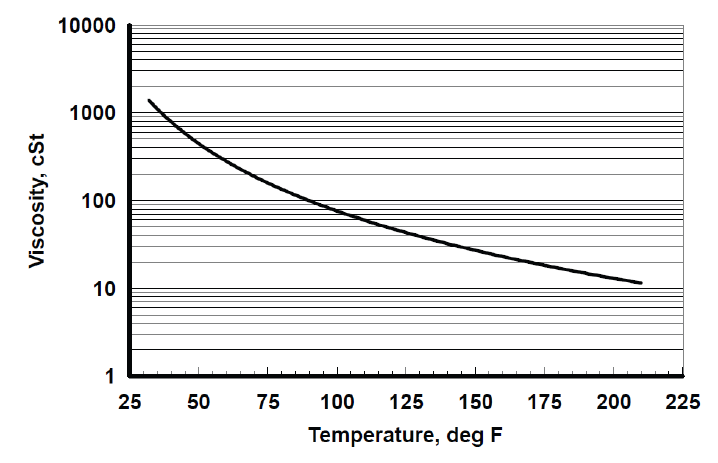
Viscosity, cSt 32°F 77°F 100°F 210°F 1100 160 80 11
Safety & Health
- Safety Considerations
Most VORANOL™ polyols generally present no significant hazard in use when simple precautions are followed. However, some VORANOL™ polyols are hazardous. Before working with VORANOL™ polyols it is necessary to understand the hazards involved in handling all of the components, and to establish and follow safe work procedures. Material Safety Data Sheets, product literature, and safe handling and storage information are available for the polyurethane materials supplied by Dow. Recommendations for handling, storage and disposal of any ingredient not furnished by Dow should be acquired from the supplier.
Toxicity and First Aid
Skin and Eyes
When working with VORANOL™ polyols, avoid contact of polyol with eyes or skin. Safety glasses are suggested for use with most polyols, however, some VORANOL™ polyols require that chemical workers’ goggles be worn. Skin contaminated with polyols should be washed with soap and plenty of water. If polyol contacts eyes, flush with plenty of low pressure flowing water. If irritation occurs from contact with polyols, get medical attention.Ingestion
Polyols are low to very low in acute oral toxicity. If a polyol is swallowed, give large amounts of water to dilute. Obtain medical attention.Inhalation
VORANOL™ polyols typically do not present a significant problem from inhalation. If any adverse effects should occur, get the affected person to fresh air and obtain medical attention.Fire and Explosion
VORANOL™ polyols will burn under certain conditions and can explode if heated to decomposition temperature in a confined area. VORANOL™ polyols are Class IIIB Combustible Liquids under OSHA. Polyol fires can be extinguished with water fog, carbon dioxide or dry chemicals. Polyol fires not involving isocyanate may be extinguished with alcohol foam. Personnel fighting isocyanate fires or polyol fires involving isocyanate should wear pressure demand, self-contained breathing apparatus and full protective clothing as protection against nitrogen dioxide fumes and isocyanate vapors.Spills and Disposal
Waste polyol should be burned in an adequate incinerator. Landfill disposal of polyols is not recommended because of the chemical’s water solubility. Waste disposal of either isocyanate or polyol should always be in accordance with federal, state and local environmental laws and regulations.
